Are you wondering how to extract BOM of parametric pipe support correctly?
If you’re working with custom parametric pipe supports in AutoCAD Plant 3D and struggling to generate a Bill of Materials (BOM) — you’re not alone. One common issue is that even after creating parametric components using Python, their metadata does not show up in the Piping.dcf SQL database, making BOM extraction nearly impossible through traditional means.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to extract BOM of parametric pipe support correctly — using the PipeRouting SDK API, sample DLLs, and external tools. Whether you’re a beginner or an intermediate developer, this post outlines everything you need to know to succeed.
Table of Contents
What’s the Problem with SQL BOM in Plant 3D
When you create parametric pipe supports using Python or Plant 3D’s custom scripting, your dimensions (L1, H1, W1, etc.) are stored as part of the component geometry — but not written into the SQL database (Piping.dcf). As a result, your custom parts may show up in the project, but their dimensional data will not appear in standard BOM tables or reports.
Here’s a visual breakdown of this issue:
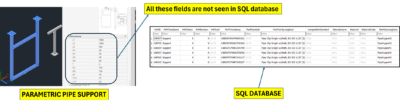
Dimensions like L1, H1, and W1 are visible in the support model but do not appear in the SQL database. This prevents automatic BOM generation for parametric parts.
The Right Way to Extract BOM of Parametric Pipe Support
To extract BOM data for these supports, Autodesk recommends using the PipeRouting SDK API provided through its AutoCAD Plant 3D developer tools.
This API allows you to:
-
Access and read geometry parameters
-
Use commands like
FittingEditto modify and extract dimensions -
Export the data to Excel or include them in custom BOM reports
This method does require some knowledge of .NET (C#) programming, but it’s currently the only supported way to access parametric pipe support data programmatically.
Step-by-Step: Load PipeRouting SDK DLL in Plant 3D
Follow these steps to set up and use the SDK:
Step 1: Download the SDK
Get the AutoCAD Plant 3D SDK from Autodesk APS:
https://aps.autodesk.com/developer/overview/autocad-plant-3d-and-pid
Step 2: Load the DLL in AutoCAD Plant 3D
-
Open AutoCAD Plant 3D.
-
Use the
NETLOADcommand. -
Browse to:
PipeRouting\bin\x64\Debug\PipeRouting.dll -
Load the DLL.
Once loaded, you’ll be able to use the commands provided by the SDK.
Use the FittingEdit Command to Access Dimensions
After loading the DLL, try using the FittingEdit command to select your custom pipe support in the drawing. This lets you:
-
View the dimension parameters (L1, H1, etc.)
-
Modify or extract values
-
Extend functionality using C# scripts
Available SDK Commands:
-
PipeRoute -
FittingAdd -
FittingEdit -
FittingSubstitute
If
FittingEditdoes not show up, check that the correct DLL was built and loaded using Visual Studio.
How to Export to Excel or Report/Isometric
You now have the dimensions — but how do you use them in reports?
Option 1: Export to Excel
-
Modify the C# SDK code to write values to
.xlsx -
Use libraries like
EPPlusorClosedXML
Option 2: Add to BOM / Reports
-
Extend the report schema to include new custom fields
-
Create custom Report Creator templates in Plant 3D
-
Optionally, script isometric annotations
Exporting to isometric drawings may require editing the Isoconfig.xml or using Project Setup tools.
Helpful Links and Resources
Key Takeaways
-
Parametric support dimensions are not saved to the SQL database by default.
-
To extract them, you must use the PipeRouting SDK API and C# programming.
-
Once accessed, you can export the data to Excel or use them in custom BOM reports.
-
Autodesk has not yet enabled this as a built-in feature — but several community threads are pushing for it.
Related Posts You May Like
Need AutoCAD Plant 3D for Learning or Projects?
Explore our affordable AutoCAD Plant 3D options at UpkeyStore, perfect for students and professionals working with piping and plant design.











